 GLOSSARIO
GLOSSARIO GLOSSARIO
GLOSSARIO
Nomenclatura Chimica: commerciale e IUPAC
Amorphous - having no ordered
arrangement. Polymers are amorphous when their chains are tangled up in
any old way. Polymers are not amorphous when their chains are lined
up in ordered crystals. (see: crystal)
Amorfo - senza alcun
ordine definito. I polimeri sono amorfi quando le loro catene sono aggrovigliate.
I polimeri non sono amorfi quando le loro catene sono ben allineate in
cristalli ordinati.. (vedi: cristalli)
Anion - an atom or molecule
which has a negative electrical charge. (see: ion)
Anione - un atomo
o una molecola con carica elettrica negativa. (vedi: ione)
Cation - an atom or molecule
which has a positive electrical charge. (see: ion)
Catione - un atomo
o una molecola con carica elettrica positiva (vedi: ione)
Complex - two or more molecules
which are associated together by some type of interaction of electrons,
other than a covalent bond. (see:
covalent bond)
Complesso - due o
più molecole che si associano attraverso un certo tipo di interazione
degli elettroni diversa dal legame covalente (vedi: legame
covalente)
Covalent bond - a joining
of two atoms when the two share a pair of electrons.
Crosslinking - crosslinking
is when individual polymer chains are linked together by covalent bonds
to form one giant molecule. (see:
elastomer,
thermoset)
Crystal - a mass of molecules
arranged in a neat and orderly fashion. In polymer crystal the chains are
lined up neatly like new pencils in a package. They are also bound together
tightly by secondary interactions. (see: secondary
interactions)
Elastomer - rubber. Hot
shot scientists say a rubber or elastomer is any material that can be stretched
many times its original length without breaking, and will snap back
to its original size when it is released.
Electrolyte - a molecule
that separates into a cation and an anion when its dissolved in a solvent,
usually water. For example, salt, NaCl separates into Na+ and
Cl- in water:
(see: anion, cation)
Elettrolita - una molecola
che si divide in catione ed anione quando viene dissolta in un solvente,
solitamente acqua. Ad esempio il sale, NaCl si divide in Na+ e Cl<sup-
in acqua. (vedi: anione, catione)
Elongation - how long a sample
is stretched when it is pulled. Elongation is usually expressed as the
length after stretching divided by the original length.
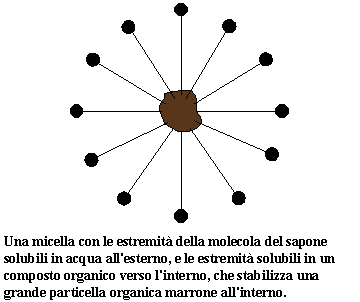
Emulsion - a mixture in which
two immiscible substances, like oil and water, stay mixed together thanks
to a third substance called an
emulsifier. The emulsifier is usually
something like a soap, whose molecules have a water-soluble
end and an organic-soluble end. The soap molecules form little balls called
micelles,
in which the water-soluble ends point out into the water, and the organic-soluble
ends point into the inside of the ball. The oil is stabilized in the water
by hiding in the center of the micelle. Thus the water and oil stay mixed.
Una micella con le estremità
della molecola del sapone solubili in acqua all'esterno, e le estremità
solubili in un composto organico verso l'interno, che stabilizza una grande
particella organica marrone all'interno. Emulsione - una miscela
nella quale due sostanze che non si possono mescolare come olio ed acqua,
si mescolano grazie ad una terza sostanza denominata emulsionante.
L'emulsionante
è un prodotto tipo il sapone
le cui molecole hanno un'estremità solubile in acqua ed un'estremità
solubile in un composto organico. Le molecole di sapone formano piccole
sfere chiamata micelle nelle quali le estremità solubili
in acqua sono dirette verso l'acqua, e le estremità solubili in
un composto organico sono dirette verso l'interno della sfera. L'olio si
stabilizza nell'acqua nascondendosi al centro della micella. In questo
modo acqua ed olio possono mescolarsi.
Entropy - disorder. Entropy
is a measure of the disorder of a system.
First order transition - a
thermal transition that involves both a latent heat and a change in the
heat capacity of the material. (see: heat capacity,
latent
heat, second order transition,
thermal
transition)
Free radical - an atom or molecule which has at
least one electron which is not paired with another electron.
Gel - a crosslinked polymer which
has absorbed a large amount of solvent. Crosslinked polymers usually swell
a good deal when they absorb solvents. (see: crosslinking)
Gem diol - a diol in which both
hydroxy groups are on the same carbon. Gem diols are unstable. Why are
they called gem diols? It's short for geminal, which means
"twins". It's related to the word gemini.
Glass transition temperature -
the temperature at which a polymer changes from hard and brittle to soft
and pliable.
Heat capacity - the amount
of heat it takes to raise the temperature of one gram of a material one
degree Celsius.
Hydrodynamic volume - the volume
of a polymer coil when it is in solution. This can vary for a polymer depending
on how well it interacts with the solvent, and the polymer's molecular
weight.
Hydrogen bond - a very strong
attraction between a hydrogen atom which is attached to an electronegative
atom, and an electronegative atom which is usually on another molecule.
For example, the hydrogen atoms on one water molecule are very strongly
attracted to the oxygen atoms on another water molecule.
L'idrogeno
con una carica positiva parziale è attratto dall'ossigeno con la
sua carica negativa parziale
Ion - an atom or molecule which
has a positive or a negative electrical charge.
Latent heat - the heat given
off or absorbed when a material melts or freezes, or boils or condenses.
For example, when ice is heated, once the temperature reaches 0 oC,
it's temperature won't increase until all the ice is melted. The ice has
to absorb heat in order to melt. But even though it's absorbing heat, it's
temperature stays the same until all the ice has melted. The heat required
to melt the ice is called the latent heat. The water will give off
the same amount of latent heat when you freeze it.
Le Chatelier's principle -
this principle states that if a system is placed under stress, it will
act so as to relieve the stress. Applied to chemical reactions, it means
that if product or byproduct is removed from the system, the equilibrium
will be upset, and the reaction will produce more product to make up for
the loss. In polymerizations, this trick is used to make polymerization
reactions reach high conversion.
Ligand - an atom or group
of atoms which is associated with a metal atom in a complex. Ligands may
be neutral or they may be ions. (see: complex,
ion)
Living polymerization
- a polymerization reaction in which there is no termination, and the polymer
chains continue to grow as long as there are monomer molecules to add to
the growing chain.
Matrix - in a fiber reinforced
composite, the matrix is the material in which the fiber is embedded, the
material that the fiber reinforces. It comes from a Latin word which means
"mother", interestingly enough.
Modulus - the ability of
a sample of a material to resist deformation. Modulus is usually expressed
as the ratio of stress exerted on the sample to the amount of deformation.
For example, tensile modulus is the ration of stress applied to the elongation
which results from the stress. (see: elongation,
stress)
Monomer - a small molecule which
may react chemically to link together with other molecules of the same
type to form a large molecule called a polymer.
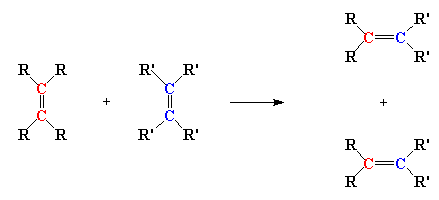
Olefin Metathesis - a
reaction between to molecules, both containing carbon-carbon double bonds.
In olefin metathesis, the double bond carbon atoms change partners, to
create two new molecules, both containing carbon-carbon double bonds.
Oligomer - a polymer whose
molecular weight is too low to really be considered a polymer. Oligomers
have molecular weights in the hundreds, but polymers have molecular weights
in the thousands or higher.
Plasticizer - a small molecule
that is added to polymer to lower its glass transition temperature. (see:
glass
transition temperature).
Random coil - the shape of a
polymer molecule when its in solution, and it's all tangled up in itself,
instead of being stretched out in a line. The random coil only forms when
the intermolecular forces between the polymer and the solvent are equal
to the forces between the solvent molecules themselves and the forces between
polymer chain segments.
Molecola di polimero aggrovigliata a forma di spirale irregolare
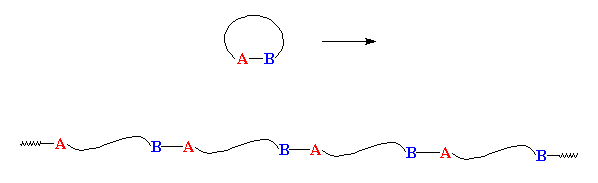
Ring-opening polymerization
- a polymerization in which cyclic monomer is converted into a polymer
which does not contain rings. The monomer rings are opened up and stretched
out in the polymer chain, like this:
Secondary interaction -
interaction between two atoms or molecules other than a covalent bond.
Secondary interactions include hydrogen bonding, ionic interaction, and
dispersion forces. (see: hydrgoen bond)
Second order transition - a
thermal transition that involves a change in heat capacity, but does not
have a latent heat. The glass transition is a second order transition.
(see: first order transition, glass
transition temperature, heat capacity,
latent
heat, thermal transition)
Soap - a molecule in which one
end is polar and water-soluble and the other end is non-polar and organic-soluble,
such as sodium lauryl sulfate:
Strain - the amount of deformation
a sample undergoes when one puts it under stress. Strain can be elongation,
bending, compression, or any other type of deformation. (see: elongation,
stress)
Strength - the amount of
stress an object can receive before it breaks. (see: stress)
Stress - the amount of force
exerted on an object, divided by the cross-sectional area of the object.
The cross-sectional area is the area of a cross-section of the object,
in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the force. Stress is usually
expressed in units of force divided by area, such as N/cm2.
Termination - in a chain
growth polymerization, the reaction which causes the growing chain to stop
growing. Termination reactions are reactions in which none of the products
may react to make a polymer grow.
Thermoplastic - a material
that can be molded and shaped when it's heated.
Thermal transition - a change
that takes place in a material when you heat it or cool it, such as melting,
crystallization, or the glass transition. (see: glass transition
temperature)
Thermoset - a hard and stiff
crosslinked material. Thermosets are different from thermoplastics,
which become moldable when heated. Thermosets are crosslinked, so they
don't. Also, they are different from crosslinked elastomers. Thermosets
are stiff and don't stretch the way elastomers do. (see: elastomer,
thermoplastic)
Toughness - a measure of the
ability of a sample to absorb mechanical energy without breaking, usually
defined as the area underneath a stress-strain curve. (see: stress,
strain)
Transesterification - A reaction between an ester
and an alcohol in which the -O-R of the ester and the -O-R' group of the
alcohol trade places, as shown below.
Legame covalente
- unione di due atomi quando gli stessi hanno in comune una coppia di elettroni
Reticolazione - si
ha una reticolazione quando le catene di un singolo polimero sono legate
insieme da legami covalenti e formano una molecola gigante. (vedi
elastomero,
termoindurente)
Cristallo - una massa
di molecole disposte in modo armonioso ed ordinato. Nei cristalli polimerici
le catene sono allineate in modo ordinato come le matite disposte nella
loro confezione. Sono legati insieme strettamente da interazioni secondarie
(vedi: interazioni
secondarie)
Elastomero- gomma.
I grandi scienziati anglosassoni definiscono gomma o elastomero qualsiasi
materiale che, allungato, può raggiungere lunghezze molte volte
superiori alla sua lunghezza originaria senza rompersi e che ritorna immediatamente
alla sua lunghezza originaria quando viene rilasciato.
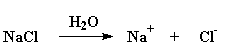
>Allungamento - variazione
dimensionale di un campione quando viene tirato. l'allungamento è
normalmente definita come la lunghezza del campione dopo lo stiramento,
divisa per la lunghezza originale.
Entropia - disordine.
L'entropia è la misura del disordine di un sistema.
Transizione di primo
ordine - transizione termica che coinvolge sia il calore latente che
un cambiamento di calore specifico del materiale. (vedi: calore
specifico, calore
latente, transizione
di secondo ordine, transizione
termica)
Radicale libero -
atomo o molecola che ha almeno un elettrone non accoppiato ad un altro
elettrone
Gel - polimero reticolato
che ha assorbito una grande quantità di solvente. I polimeri reticolati
aumentano molto di volume quando assorbono i solventi. (vedi: reticolazione)
Diolo geminale (gem diolo)
- un diolo in cui entrambi i gruppi idrossilici sono sullo stesso atomo
di carbonio. I dioli geminali. sono instabili. Perché vengono definiti
gem dioli? E' un abbreviazione di geminale che significa "gemelli".
Deriva dalla parola gemini.
Temperatura di transizione
vetrosa - temperatura alla quale un polimero da resistente e fragile
diventa soffice e flessibile.
Calore specifico -
quantità di calore necessario per aumentare di un grado celsius
un grammo di materiale
Volume idrodinamico
- volume di un gomitolo polimerico in una soluzione. Può variare
nei polimeri a seconda di come interagisce con il solvente e secondo il
peso molecolare del polimero.
Legame idrogeno -
un'attrazione molto forte tra un atomo di idrogeno che è legato
ad un atomo elettronegativo ed un atomo elettronegativo che normalmente
si trova su un'altra molecola. Ad esempio gli atomi di idrogeno su una
molecola d'acqua sono attratti dagli atomi di ossigeno su un'altra molecola
d'acqua.

Ione - atomo o molecola
con carica elettrica positiva o negativa
Calore latente -
calore rilasciato o assorbito quando un materiale fonde o gela, bolle o
si condensa. Ad esempio quando il ghiaccio viene riscaldato, una volta
raggiunta la temperatura di 0°C, la sua temperatura non aumenterà
fino a quando il ghiaccio non si è sciolto. Il ghiaccio deve assorbire
calore per sciogliersi. Ma anche se assorbe calore la sua temperatura rimane
la stessa fino a quando non si è sciolto. Il calore necessario per
sciogliere il ghiaccio viene definito calore latente. L'acqua rilascerà
la stessa quantità di calore quando viene congelata.
Principio di Le Chatelier's-
questo principio afferma che se un sistema viene sollecitato, agirà
in modo tale da liberarsi della sollecitazione. Applicato alle reazioni
chimiche significa che se un prodotto od un sottoprodotto viene rimosso
dal sistema l'equilibrio viene disturbato e la reazione produrrà
una maggiore quantità di prodotto per compensare la perdita. Nelle
polimerizzazioni, questo principio viene utilizzato per fare in modo che
le reazioni di polimerizzazione raggiungano una elevata conversione.
Legante - atomo o
gruppo di atomi associati ad un atomo di metallo in un complesso. I leganti
possono essere neutri o ioni . (vedi: complesso,
ione)
Polimerizzazione vivente
- reazione di polimerizzazione in cui non avviene la terminazione e le
catene polimeriche continuano a crescere fino a quando ci sono molecole
di monomero da aggiungere alle catene.
Matrice - in un composito
rinforzato da fibre, la matrice è il materiale nel quale la fibra
è inglobata, il materiale rinforzato dalla fibra. Deriva dal termine
latino che significa "madre".
Modulo - la capacità
di un materialedi resistere alla deformazione. E' normalmente indicato
come il rapporto tra la sollecitazione applicata al campione, rispetto
alla deformazione. A titolo di esempio, il modulo tensile è
il rapporto tra la forza applicata e l'allungamento che ne risulta. (vedi:
allungamento,
sollecitazione)
Monomero - piccola
molecola che può reagire chimicamente per legarsi con altre molecole
dello stesso tipo e formare molecole più grandi dette polimeri
Metatesi delle olefine -
reazione tra due molecole, contenenti entrambe doppi legami carbonio-carbonio.
Nelle metatesi delle olefine gli atomi di carbonio a doppio legame cambiano
partner, per creare due nuove molecole contenenti entrambe i doppi legami
carbonio-carbonio.
Oligomero - polimero
il cui peso molecolare è troppo basso per essere considerato effettivamente
un polimero. Gli oligomeri hanno pesi molecolari nell'ordine delle centinaia
ma i polimeri hanno pesi molecolari nell'ordine dellei migliaia o più.
Plastificante - additivo
che viene aggiunta al polimero per abbassare la sua temperatura di transizione
vetrosa (vedi: temperatura
di transizione vetrosa).
Gomitolo statistico
- forma di una molecola di polimero in una soluzione, completamente avvolta
intorno a se stessa invece di essere ben distesa formando una linea. La
spirale irregolare si forma solo quando le forze intermolecolari tra il
polimero ed il solvente sono uguali alle forze tra le stesse molecole del
solvente e alle forze tra i segmenti della catena polimerica.

Polimerizzazione con
apertura d'anello - polimerizzazione nella quale il monomero ciclico
è convertito in un polimero che non contiene anelli. Gli anelli
di polimero sono aperti e allungati nella catena polimerica come questi:
Interazione secondaria
- interazione tra due atomi o molecole diversa dal legame covalente. Le
interazioni secondarie comprendono il legame idrogeno, l'interazione ionica
e le forze di dispersione (vedi: legame
idrogeno)
Transizione di secondo
ordine - transizione termica nella quale si ha un cambiamento della
calore specifico, ma non vi è calore latente. La transizione vetrosa
è una transizione di secondo grado (vedi: transizione
di primo ordine, temperatura
di transizione vetrosa, calore
specifico, calore
latente, transizione
termica)
These form micelles in water, little balls in which the
polar ends of the molecules point out into the water, and the non-polar
ends point inward, away from the water. Water insoluble dirt can hide inside
the micelle, so soapy water washes away dirt that plain water can't. (see
emulsion)
Tensioattivo - molecola
nella quale una estremità è polare e solubile in acqua e
l'altra estremità è non-polare e solubile in un composto
organico come il sodio lauril solfato.
Forma micelle nell'acqua,
piccole sfere nelle quali le estremità polari delle molecole sono
dirette verso l'acqua e le estremità non polari sono rivolte verso
l'interno, lontano dall'acqua. Lo sporco non solubile in acqua può
nascondersi all'interno delle micelle, ecco il motivo per cui l'acqua unità
al tensioattivo elimina la sporcizia che l'acqua pura non riesce ad eliminare.
(Vedi emulsione.)
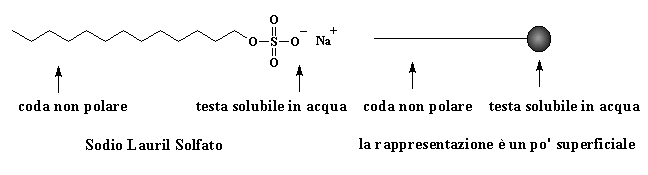
Rappresentazione
Sodio Lauril Solfato: coda non polare e testa solubile in acqua; a destra
la rappresentazione è un po' superficiale.
Deformazione - la deformazione di un campione quando esso viene sottoposto ad uno sollecitazione.
La deformazione può essere allungamento, flessione, compressione
o qualunque altro tipo di deformazione.
Carico - sollecitazione
che un oggetto può sopportare prima di rompersi. (vedi sollecitazione)
Sollecitazione - La
quantità di forza esercitata su un oggetto, diviso per la sezione
trasversale dell'oggetto stesso. L'area della sezione trasversale
è l'area di una sezione su un piano parallelo alla direzione della
forza. La sollecitazione è normalmente espressa in unità
di forza divise per l'area, come in N/cm2.
Terminazione - in
una polimerizzazione a catena, è la reazione che provoca l'arresto
della crescita delle catene. Le reazioni di terminazione sono quelle in
cui nessuno dei prodotti può reagire per far crescere un polimero.
Termoplastico - materiale
che può essere stampato e modellato se riscaldato
Transizione termica
- cambiamento che si verifica in un materiale quando viene riscaldato o
raffreddato, come nella fusione, nella cristallizzazione o nella transizione
vetrosa (vedi: temperatura
di transizione vetrosa)
Termoindurente -
materiale reticolato resistente e rigido. I termoindurenti sono diversi
dai termoplastici che possono essere modellati se riscaldati. I
termoindurenti sono reticolati, quindi non possono essere modellati. Sono
inoltre diversi dagli elastomeri vulcanizzati. I termoindurenti
sono rigidi e non si allungano come gli elastomeri (vedi elastomero, termoplastico)
Tenacità -
è una misura della capacità di un campione ad assorbire l'energia
meccanica senza rompersi; normalmente è definita dall'area sottostante
la curva sforzo-deformazione. (see: sollecitazione,
deformazione)
Transesterificazione
- Reazione tra un estere ed un alcool nel quale il gruppo O -R dell'estere
e il gruppo O - R' dell'alcool si scambiano il posto come rappresentato
qui di seguito.
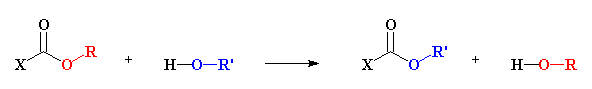
 Ritorna all'Indice della Macrogalleria
Ritorna all'Indice della Macrogalleria